Students should have already learned:
· The fundamental concepts of voltage, current, and resistance.
· Ohm’s Law: V / I = R (voltage / current = resistance).
· Characteristics and measurements of resistance, current & voltage for series circuit
I = I1= I2= I3……
R = R1 + R2+ R3+……
V = V1 + V2+ V3+……
V1 / R1 = V2/R2……
·
![]() Voltmeter (measures voltage)
Voltmeter (measures voltage)
· ![]() Ammeter (measures current)
Ammeter (measures current)
· ![]() A battery (6 volts)
A battery (6 volts)
·
![]() A limited set of resistors
A limited set of resistors
· A resistor color-code chart
· Wires and connectors -------------------
·
Three copper-wires of different length ( 6cm, 8cm,10cm)

Note: The connectors and unknown wire should be made of different materials.
For this activity, make groups of four heterogeneous students. Assign these roles to the students: material manager, observer, recorder, and timekeeper.
· Student will connect the circuit as shown below; teacher will facilitate the students and make sure that the connections are right.
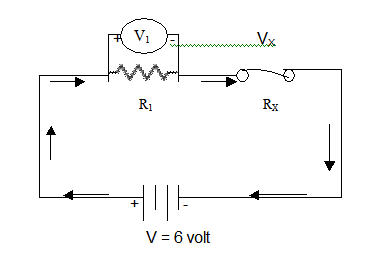
V = 6 volt
· Measured the voltageV1 across the known resistor R1 through voltmeter
· Connect the copper wire of unknown resistor Rx as shown in the circuit.
· Replace the copper wire of different length for each observation.
· Calculate the value of Vx across an unknown resistor by using the characteristics of voltage for series circuit i-e V = V1+Vx
· Calculate the value of an unknown resistor Rx by using Ohm’s law and the characteristics of current for a series circuit
V1 / R1= I Vx / Rx= I \I = I1= Ix
\ V1 / R1 = Vx / Rx
Rx = V1 × Vx / R1
Observations and Calculations
V = 6volts
|
#of Observation
|
V1 Measured Voltage drop across R1
(volt)
|
Known resistor R1
(ohm)
|
Vx Voltage across unknown resistor Rx Vx = V-V1 (volt)
|
Unknown resistance Rx of variable length V1Rx = Vx R1 Rx =Vx R1/V1 (ohm)
|
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 |
Discussions and Assessment
Teacher will facilitate the discussion by walking around and asking some key questions in the groups. For example,
Q. Why does the voltage drop V1 change across the resistor R1 by changing the length of the unknown resistor Rx?
Q. How can you connect the ammeter in the circuit in order to measure the current? What does the arrow represent in the circuit?
Q. Draw a graph between the values of Vx and Rx and interpret it.
Homework
Q. What might happen to the resistance of unknown resistor of same length,
if it is replaced by wire having
1) different materials like lead, silver, or gold
2) different thickness ?
Grateful
Acknowledgment to:
Dr. Herman Irving and Justine Herrera of MRSEC
Dr. Sarbajit Banerjee and Mr. Jay Dubner, Columbia University
· To comprehend the relationship between voltage and resistance in series circuit [Teaching Standard 9-12 A - Teaching and assessment strategies, Development of student understanding]
· Make a series electrical circuit that meets given specifications. [Content Standard 9-12 E – Technological Design]
· Orally predict and physically verify electrical measurements. [Content Standard 9-12 A –Scientific inquiry]
· Complete a design task as part of a structured cooperative team. [Teaching Standard E - Nurture collaboration among students]
· Create a setting for student work that is flexible and supportive of science inquiry [Teaching Standard D – Provide students with the time, space, and resources for learning science]
· [Teaching Standard C – Engage in ongoing assessment of student learning]
· [Teaching Standard E - require students to take responsibility for the learning of all members of the community]
· [Assessment Standard B – Achievement and opportunity to learn science must be assessed]