Summer Research Program for Science Teachers
David S. Friedman
General Douglas MacArthur High School, Long Island
2002
What is pollution and what types are there?
INTRO TO POLLUTION (1 day)
DO NOW: What is pollution? Where do we find pollution?
Give students 5 minutes in groups to come up with answers, write all of the student’s logical answers on the board.
Students may discuss chemicals or substances that are added to air, water, and land.
Today we will focus on air pollution. (10 min)
Ask: What are primary pollutants?
Help students to understand that chemicals or substances emitted directly into the air are primary pollutants. If these pollutants react with other substances in the air and form a new compound they are called secondary pollutants.
(Content Standard F – Natural and human induced hazards)
Ask: Why should we care about pollution?
-We inhale 20,000 L of air/day.
-Pollution causes 150,000 premature deaths per year worldwide.
-Acute health effects: can be life threatening within hour or days or irritate preexisting conditions such as asthma.
-Chronic health effects: deterioration of health over years even with low dose or short term exposures.
-Some pollutants are known or suspected carcinogens (cause cancer). Diesel fumes are presumed carcinogens since they contain carcinogenic materials.
-Pollution can kill plants and animals and destroy buildings and outdoor artistic/historic structures. Also, discuss biomagnification.
(Content Standard F – Personal and community health/ Environmental quality; Content Standard Unifying Concepts and Processes – Evidence, models and explanation)
Discuss some types of pollutants, for example: (10 min)
1.Carbon Monoxide (CO)- forms from incomplete burning of carbon containing fuels, found in cigarette smoke and car exhaust, at low doses it causes nausea and dizziness, at high doses it causes death.
2.Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) & Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)- form from the burning of fossil fuels (gas, oil, coal), irritates lungs, causes acid rain which can destroy statues and buildings.
3.Suspended Particulate Matter- small particles that are suspended in the atmosphere that at times can be seen as dust, smoke, and haze… caused by burning of fuels (DIESEL is a major contributor)… they may irritate lungs and cause aggravation of asthma… some particulates are thought to be carcinogenic (cause cancer).
(Content Standard F – Personal and community health / Environmental quality / Science and technology in local, national and global challenges / Natural resources)
Have students work in groups to discuss how pollution levels can be controlled…. They should try and think about how they themselves can reduce pollution and how the community at large can work together to reduce levels.
(Content Standard F – Science and technology in local, national, and global challenges; Content Standard G – Science as a human endeavor)
For example: Reduce, reuse, and recycle…. Push for hybrid and electric vehicles…(10 min)
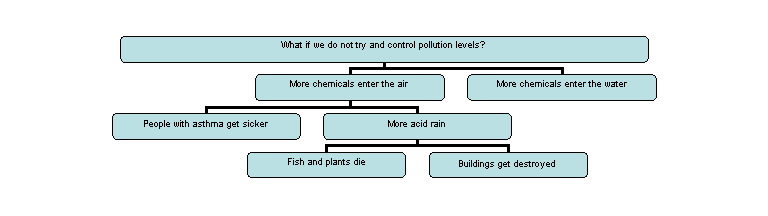
Have students work in groups and come up with “WHAT IF.…..?” webs for questions such as, “What if we do not try and control pollution levels?”
For example:

(Content Standard F)
Return to the Earth Science Lesson Plan Menu