How
does a pedigree help us to trace a trait that is inherited?
Nakita McNeil
Independence High School,
Manhattan
Summer Research Program for Science Teachers
Summer 2008
Objective: Students will be able to
analyze genetic (basic) patterns to determine dominant or recessive inheritance,
summarize examples of dominant and recessive disorders, and construct a human
pedigree from genetic information.
Time: 1-2
class sessions
1.Do
Now:
Face a partner. Observe your partner.
List features about you partner that makes them different.
Ask students:
Are we all the same? Where do traits come from?
2. Vocabulary:
Inheritance
Trait
Heredity
3.
LESSON
Brainstorm, and ask students: What are some traits that are
passed down in their family’s lineage?
(Students must remember that certain characteristics about
a person [weight] can be altered by environmental factors and should not be
placed in the heredity column).
4. Teacher lead instruction (demonstrate)
Teacher
:
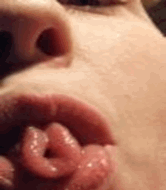
How many of you (students) can
role your tongue?
Being able to role you tongue is a dominant expression of a
gene. “It shows”
Teacher:
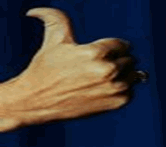
How many of you (students) have a hitchhikers thumb?
Hitchhikers thumb is a recessive
(hidden) expression of a gene
Teacher:
How
many students have a widow’s peak?
Widows peak
is a dominant (shown) expression
of a gene.

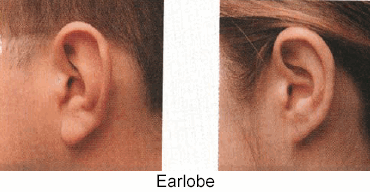
Teacher: How many students have connected earlobes?
Free earlobes are a dominant
expression of a gene.
Have your students test their partner again now that they
know some basics traits
|
Trait
|
You
YES
|
NO
|
Your partner
YES
|
NO
|
|
|
|
Are you Female?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Are you Right Handed?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do you handclasp with your right
thumb on top?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do you have Attached Ear lobes?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Can you roll your tongue?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do you have a Widow's Peak?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do you have a Cleft Chin?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do you have a Hitch Hiker's Thumb?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Do you have Cheek Dimples?
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.
Anticipation Guide
Directions: For each of the
following questions state if you agree or disagree and tell why.
-
If you are a girl, you inherit more from your mother.
If your parents can both roll their tongues, you will certainly be able
to roll your tongue.
A parent may give a trait to his child without ever having the trait
himself.
If you are injured (hurt) in an accident, you may pass it on to your
children.
If you look more like one parent than the other, you inherited more from
that parent.
At birth, you have all the hereditary traits you are ever going to have.
6.
Ask: Are there any traits
that you are sure you inherited from your parents?
|
Trait
|
Who you
inherited it from
|
|
Eye color, shape, size
|
Mother
|
|
Hair texture
|
Grandfather
|
7. Look at the following pedigree that shows my
relationship to other members of my family.
List 3 things you can learn about my
family by looking at this chart. (I have chosen to put stars in the shapes that
are affected, because I want to first emphasize male vs. female, then redraw
shaded vs. not shaded)
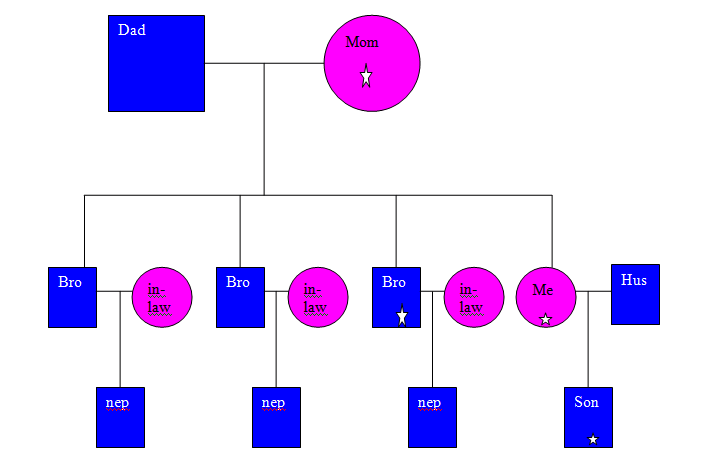
Realize all males are in blue (square) and all females
(circle) are in pink. Those with stars have a widows peak.
Symbols (for
teacher) (DO NOT introduce all symbols to students – KEEP IT SIMPLE):
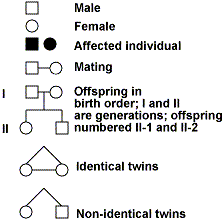
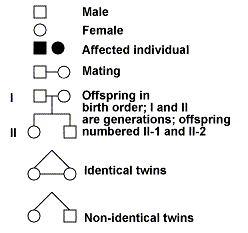
When introducing
the pedigree chart establish:
-
the symbols that are used in pedigrees.
-
words used to describe basic family relationships.
-
definitions of key words (see vocabulary list).
-
that vertical lines distinguish ‘generations’. (For example: old vs. young,
past vs. present)
-
that horizontal lines represent the same ‘generation’.
-
the difference between a relative and an ancestor.
|
Vocabulary:
-
Trait
-
Inherited
-
Heredity
-
Pedigree
-
Generation
-
Relative
-
Ancestor
|
Relationships:
-
Grandmother/ma
-
Grandfather/pa
-
Mother/ma/mom
-
Father/dad/pa
-
Brother
-
Sister
-
Son
-
Daughter
-
Grandson
-
Granddaughter
-
Cousin
-
Nephew
-
Niece
-
Husband
-
Wife
|
|
In-Laws
(Marriage)
-
Mother-in-law
-
Father-in-law
-
Son-in-law
-
Daughter-in-law
-
Brother-in-law
-
Sister-in-law
|
Step
-
Stepmother
-
Stepfather
-
Stepson
-
Stepdaughter
-
Stepbrother
-
Stepsister
|
HOMEWORK: DRAW A SIMPLE PEDIGREE OF YOUR FAMILY AND TRACE A TRAIT THAT FLOWS
THROUGHOUT. NO LESS THAN THREE GENERATIONS, SHADE IN ALL THOSE WHO HAVE THE
TRAIT. FOLLOW THE PEDIGREE KEY GIVEN IN CLASS. BE PREPARED TO SHARE AND TO
DISSECT A MORE COMPLICATED PEDIGREE TOMORROW.
STANDARDS:
New York State
Science Learning Standards; Living Environment
Standard 1
Key Idea 1
1.2a Inquiry involves
asking questions and locating, interpreting, and processing
information from a
variety of sources.
1.2b Inquiry involves
making judgments about the reliability of the source and
relevance of information.
Standard 4
Key idea 2
2.1b Every organism
requires a set of coded instructions for specifying its traits. For offspring to
resemble their parents, there must be a reliable way to transfer information
from one generation to the next. Heredity is the passage of these instructions
from one
generation to
another.
2.1c Hereditary
information is contained in genes, located in the chromosomes of each cell. An
inherited trait of an individual can be determined by one or by many genes, and
a single gene can influence more than one trait. A human cell contains many
thousands
of different genes in its nucleus.
Key idea 3
3.1b New inheritable
characteristics can result from new combinations of existing genes or from
mutations of genes in reproductive cells.
Key Idea 5
5.2h Disease may also
be caused by inheritance, toxic substances, poor nutrition, organ malfunction,
and some personal behavior. Some effects show up right away; others may not show
up for many years.
National Science Education Standards
Content Standard A, Abilities to do scientific inquiry,
Understandings about scientific inquiry
Content Std C, The cell, The molecular basis of heredity,
matter energy organization in living systems







