Lifesaver Protein Modeling
Kalamazoo Area Science and Math Center, Michigan
Summer Research Program for Science Teachers
August 2011
Subject:
Living Environment (Biology) or AP Biology
Grade Levels: 9th to 12th
Aim:
Protein Synthesis is the process that describes how enzymes and other proteins are made from DNA
Traits are the end products of metabolic processes regulated by enzymes
Materials: For each group of 4 students
One bag of winter green lifesavers
10 plastic cups, with a paperclip and a 20cm long string
In each cup place 2 red lifesavers, 1 orange, 2 green, 1 yellow, 1 purple, and 1 white lifesaver
Procedure:
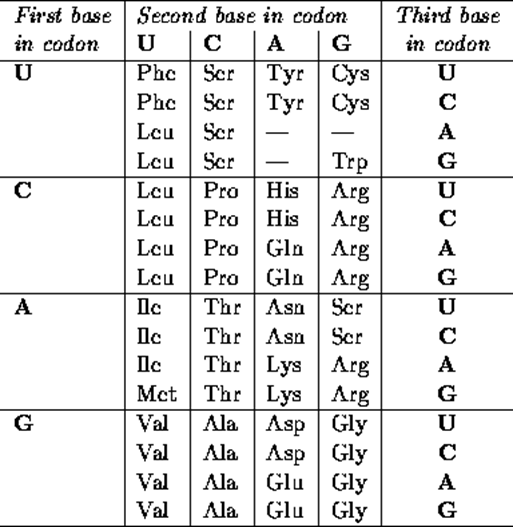
From DNA to Protein
From the following nucleotide sequence, transcribe it into mRNA on the line
beneath it. Bracket the codons and
then translate it into an amino acid sequence on the line beneath the codons.
You will be making a very short protein – only _______ amino acids long.
DNA
– TACCAA GGAAGT GCGATA CATCGT
AGCATT
mRNA-
A.A. –
Color-
1.
Compare your protein’s primary structure to the normal protein hanging on
the front board. Is your protein a
normal one? Why or why not?
2.
Is your protein a product of a mutation?
If so, which type and how can you tell?
3.
Choose 1 mRNA codons from your transcription and write their corresponding tRNA
anti-codons.
![]() mRNA codon
tRNA anti-codon
mRNA codon
tRNA anti-codon
4.
What is tRNA and why is it important in protein formation?
For
Extra Credit, research the length of the shortest protein in the human body.
What is its structure and function?
Color Code
Met
= Knot [start]
Ala
=
White
Ser
= Green
Pro
= Orange
Val
=
Red
Arg
= Yellow
Tyr
=
Purple
Stop
= Knot UAA codon
National Science Standards:
Science Content Standard A:
- Science as inquiry
B2.2x Proteins
Protein molecules are long, usually folded chains composed
mostly of amino acids and are made of C, H, O, and N.
Protein molecules assemble fats and carbohydrates; they
function as enzymes, structural components, and hormones. The function of each
protein molecule depends on its specific sequence of amino acids and the shape
of the molecule.
B2.2f Explain the role of enzymes and other proteins in
biochemical functions (e.g., the protein hemoglobin carries oxygen in some
organisms, digestive enzymes, and hormones).