Name
________________________________________
Class _________
Date _________
The Nitrogen Cycle (Student Worksheet)

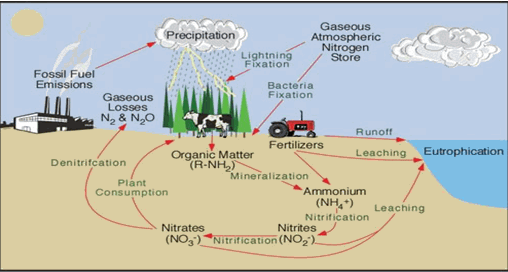
Nitrogen is an important element that is found in both the organic
(living things) and the inorganic (nonliving) parts of the Earth system.
Most of the nitrogen on Earth is found in the atmosphere.
It comprises approximately 80% of our atmosphere where it exists as
N2 gas. Nitrogen
can also be found in a variety of forms in plants, animals, soils, ocean, and
other reservoirs in the environment.
All plants and animals need nitrogen to make amino acids, proteins, and DNA, but
the nitrogen in the atmosphere is not in a form that they can use. This gas must
first be converted into a usable form during a process known as nitrogen fixation. Only specialized
bacteria in soil and certain types of algae in water can fix nitrogen.
Lightning strikes can also result in some nitrogen fixation.
Plants get the nitrogen that they need from the soil or water in which
they live. This nitrogen is usually
in the form of inorganic nitrate (NO 3-) .
Nitrate is easily dissolved in water and often leaches out of the soil.
Animals get the nitrogen that they need by consuming plants or other
animals which contain nitrogen within organic molecules.
When organisms die, their bodies decompose bringing the nitrogen into
soil or into the oceans. As these
dead organisms decompose, nitrogen is converted into inorganic forms such as
ammonium
salts (NH 4+) by a process known as
mineralization. These
ammonium salts are absorbed by the clay in the soil and are chemically altered
by bacteria into nitrite (NO 2-) and
then nitrate
(NO 3-). The
different paths in which nitrogen may follow as it cycles throughout the earth
is know as the
nitrogen cycle.
Human activities have had a huge impact in global nitrogen cycles by
causing changes in the amount of nitrogen stored in reservoirs.
The use of nitrogen-rich fertilizers can lead to nitrates from the
fertilizers washing into waterways. This increase in nitrate level can cause the
rapid growth of aquatic plants during a process known as
eutrophication. These
plants will eventually die, decompose and deplete the water of available
dissolved oxygen which can have disastrous affects on the entire food chain.
Additionally, humans are altering the nitrogen cycle by
burning fossil fuels and forests, which release nitric oxide, nitrous
oxides, and other by-products into the atmosphere where they combine with water
to form acid rain and enhance the greenhouse effect.
Test
Your Understanding
1.
Livestock
farming creates large amounts of animal waste.
How would this affect the nitrogen cycle?
2.
What would
happen if a framer used too much fertilizer?
What adverse affects can this have on the environment?
Be specific!
3. How can burning fossil fuels affect the nitrogen cycle?